
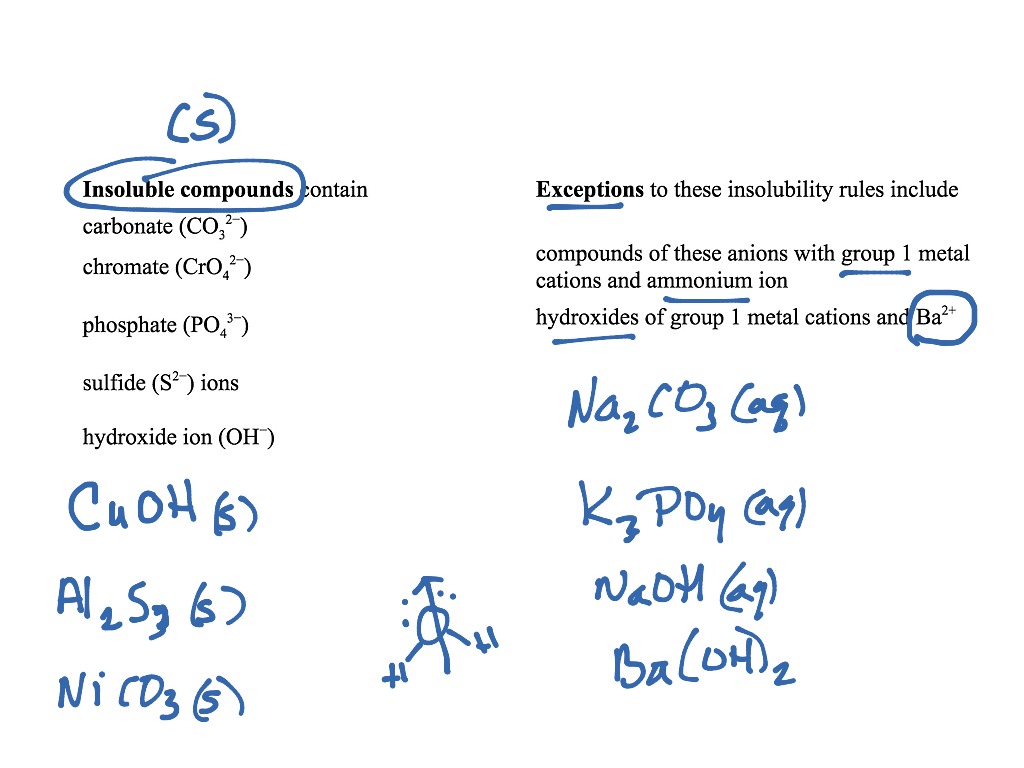
Regardless of physical state, the products of this reaction are \(Fe(OH)_3\) and \(NaNO_3\). The solubility product is given as the product of concentrations of ionic species in a solution. Higher the Ksp, higher the solubility of that substance. The solubility product constant is given for a solution that is saturated with a substance. There is no solid precipitate formed therefore, no precipitation reaction occurs.ġ. It indicates the solubility of a substance (how much of solid is dissolved in a solution). This particular example is important because all of the reactants and the products are aqueous, meaning they cancel out of the net ionic equation. Cancel out all spectator ions (those that appear as ions on both sides of the equation.):Ĭo 2 - ( aq) + 2Cl -( aq) + 2Na + ( aq) + SO 4 2 -( aq) → Co 2 - ( aq) + SO 4 2 -( aq) + 2Na + ( aq) + 2Cl -( aq) Separate the species into their ionic forms, as they would exist in an aqueous solution. Most of the precipitation reactions that we will deal with involve aqueous salt solutions. A precipitation reaction is one in which dissolved substances react to form one (or more) solid products. Note: The appearance of red precipitate confirms the presence of carbohydrates. The copper ions present in fehling’s solution in +3 state is reduced to +2 oxidation state and in alkaline medium it is precipitated as red cuprous oxide. The most common examples of precipitation are Rain, Snowfall, hail, sleet, dew etc.\] Precipitation Reactions and Solubility Rules. The formation of red precipitate confirms the presence of reducing sugars. Question: What are examples of precipitation occur in nature?Īnswer: The precipitation occurs in nature, Type and size of ions, the concentration of an aqueous solution, pH of the solution, solubility etc. Question: What are the factors that affect the precipitation reaction?Īnswer: Factors affecting precipitation reaction are, It is a type of double displacement reaction. To determine if a precipitate will form you should know the ions involved and be able to apply the solubility rules. It is used to check out elements present in the solution.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/precipitate-58e7c0c75f9b58ef7e138141.jpg)
The precipitate is shown by the down arrow in the chemical reaction. A simple set of rules, known as solubility rules, allows us to predict when a precipitation reaction will occur. NOTE: when working with precipitation reactions, the solubility rules for ionic compounds are used to determine if a precipitate forms or not. The chemical reaction in which two ions combined to form one of the insoluble products in an aqueous solution that precipitated. Frequently Asked Questions: Question: What is a precipitation reaction?

Which of the following are soluble in water SrSO4 NaNO3 PbCl2 Not soluble soluble Not soluble Precipitation Reactions When a solid doesn’t dissolve it is called insoluble. It affects by the type and size of ions, the concentration of an aqueous solution, pH of the solution, solubility etc. Except for rule 1 and 2, Sulfides are insoluble except for calcium, barium, strontium, magnesium.It is a type of double displacement reaction.
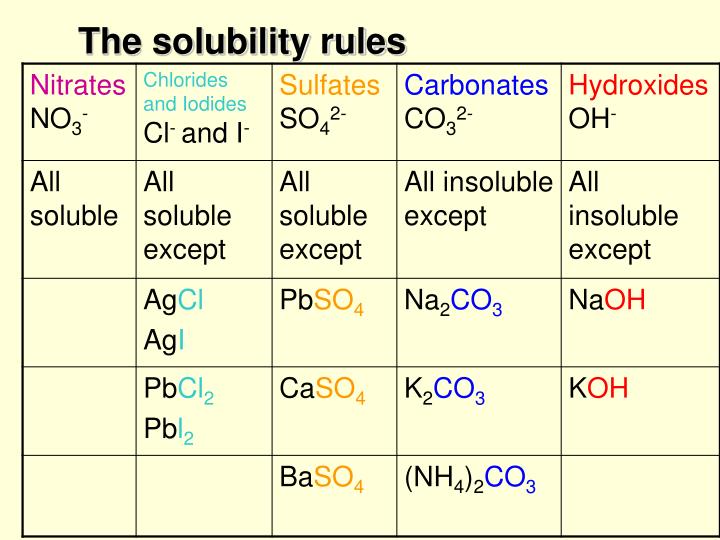
The precipitate is shown by the down arrow in a reaction.The chemical reaction in which two ions combined to form one of the insoluble products in an aqueous solution that precipitated out. The best way to complete this process and correctly predict the products is to take each of the reactants apart into their ions: Ag+ + NO3- + K+ + I- Now swap the positive ions and make the new compounds being sure to balance the charges so that the compound is neutral. Example: HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) NaCl is the salt is this reaction and you already know water.Also Read On: Alkyl Halide Examples: Detailed Insights And Facts Facts A solubility chart is a chart with a list of ions and how, when mixed with other ions, they can become precipitates or remain aqueous.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
